In the crypto space, security is everything. With hackers constantly evolving, keeping your digital assets safe requires more than just basic protection. One of the most talked-about methods of safeguarding your crypto is through something called an "air-gapped wallet." But what does this really mean, and can a truly air-gapped wallet even exist?
In this article, we’ll explore the concept of air-gapping, how it works, and whether it's truly possible to create a truly air-gapped wallet. We’ll also compare air-gapped wallets to traditional USB hardware wallets, and we’ll discuss the real-world limitations of this security method.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of air-gapped wallets and how they fit into the larger picture of crypto security.
The term "air gap" refers to a physical separation between two devices or systems. Where there is no direct connection exists between them, especially to the internet.
In simple terms, it means that one system is completely isolated from the outside world. This isolation helps protect the system from online threats, like hackers or malware since there’s no network access to exploit.
For example, when we talk about air-gapped wallets in crypto, it means the device storing your private keys has no internet connection. Because of that, it’s much harder for anyone to access or steal your information.
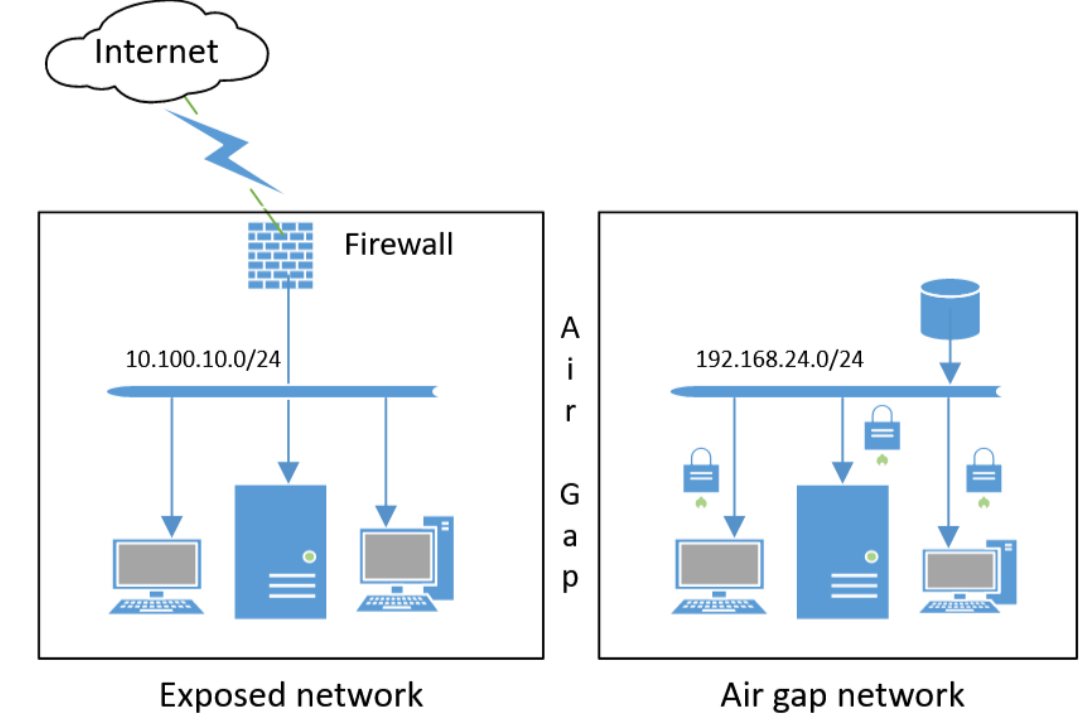
Image source- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Air_gap_(networking)#/media/File:Air_gap_network.png
An air-gapped wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that is completely isolated from the internet. It stores your private keys and other sensitive information without ever connecting to any network.
This type of wallet can be a physical device, like a hardware wallet, or a paper wallet. The key idea is that since it’s not connected to the internet, it’s much harder for hackers or malware to access your data.
Air-gapped wallets are considered one of the safest ways to store cryptocurrency as they eliminate the risk of online attacks. However, as they are completely isolated from the internet, using them involves manual steps. For example- transferring data through QR codes or SD cards instead of direct internet connections.
Air-gapped wallets have become increasingly popular as cryptocurrency users look for more secure ways to protect their digital assets. With the rise of hacking incidents and scams in the crypto space, people are becoming more cautious about storing their private keys. An air-gapped wallet offers a solution by keeping these keys offline, making it almost impossible for online attackers to access them.
As cryptocurrencies grow in value and more people invest, the need for higher security has also increased. Air-gapped wallets are appealing because they offer a level of safety that online wallets or even USB hardware wallets can’t provide. The idea of having your assets completely disconnected from the internet. It gives users peace of mind, knowing their funds are less likely to be targeted.
This rising popularity also reflects a broader trend towards decentralization and personal control over crypto security. Users want to take responsibility for their own keys without relying on third parties. Air-gapped wallets provide that secure, self-sovereign solution.
Air-gapped wallets and USB hardware wallets are both popular choices for securing cryptocurrency, but they work in different ways.
A USB hardware wallet is a device that stores your private keys offline but still requires a connection to a computer or smartphone to interact with the blockchain. While the wallet itself is offline, it briefly connects to a device during transactions. This makes it vulnerable to risks if the computer or phone is compromised by malware.
In contrast, an air-gapped wallet is entirely isolated from the internet and never connects to any device that could expose it to risks. This extra layer of isolation means there is no moment when the wallet is online, making it harder for hackers to gain access.
However, this isolation also makes air-gapped wallets a bit more complicated to use. You’ll need to manually transfer transaction data, such as signing it on the air-gapped device and then transferring it to an online device for broadcasting.
While both options offer excellent security, the key difference is the level of isolation. Air-gapped wallets are more secure from online threats, but they come with a bit more complexity in terms of use. USB hardware wallets are more convenient but still involve some exposure to potential online risks.
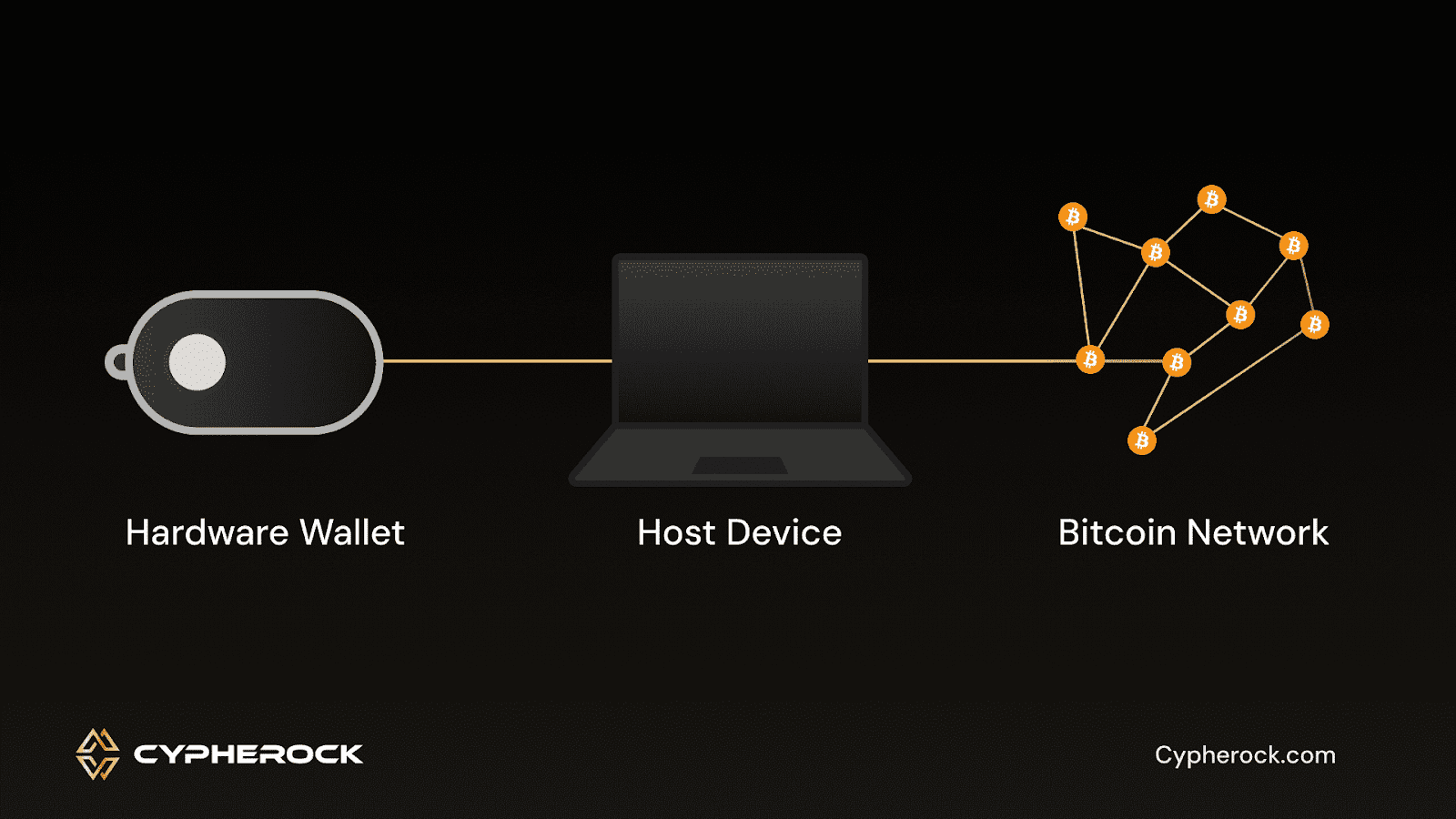
The concept of a "true" air-gapped wallet is complex and often misunderstood. Air-gapped wallets are designed to operate offline, minimizing the risk of online attacks. However, maintaining the integrity of the air gap isn't foolproof. Here's why:
Cypherock X1 redefines crypto security with its decentralized private key solution and multi-component architecture. Here's how it overcomes the challenges faced by traditional air-gapped wallets:
Most wallets store a seed phrase or private key in a single location, making them prone to loss or theft. The Cypherock X1 addresses this vulnerability by splitting private keys into five tamper-proof hardware units. Even if three units are lost or compromised, the wallet remains accessible. This approach significantly reduces the risk of device vulnerabilities, ensuring the safety of your digital assets.
Cypherock X1 avoids risky methods of data transfer like USB drives, SD cards, or QR code readers. These are often used by air-gapped wallets but can be compromised. Instead, Cypherock X1 uses NFC technology to sign transactions securely. It works without exposing your private key to the internet or any other devices, ensuring the air gap remains intact and secure.
Cypherock X1 is designed for ease of use, featuring a simple interface and guided workflows. Its OLED display and joystick navigation further reduce the likelihood of user errors. Unlike traditional wallets, which can expose sensitive information when mishandled or connected to unsafe devices, Cypherock X1 eliminates these risks. It provides secure and stress-free key management and transaction signing, making it an ideal choice for both beginners and experienced users alike.
The idea of a completely isolated, "true" air-gapped wallet is alluring but not without its challenges. While air-gapped wallets offer unparalleled protection by keeping private keys offline, they are not immune to risks. Factors like compromised data transfer tools, human error, and vulnerabilities in intermediary devices can break the isolation and expose sensitive data.
This is where Cypherock X emerges as a revolutionary solution. By eliminating single points of failure, leveraging true offline operations, and simplifying the user experience, Cypherock X1 addresses the limitations of traditional air-gapped wallets.
Its multi-component architecture and NFC-based transaction signing ensure both security and usability. Cypherock is an ideal choice for crypto enthusiasts seeking robust protection without the complexities of conventional air-gapped solutions.
The purpose of an air gap is to isolate a system or device from external networks. It is done especially on the internet, to protect it from cyber threats such as hackers and malware. This isolation helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Air gaps offer enhanced security by completely isolating devices from online threats. It reduces the risk of hacking, malware, and remote attacks. They provide a high level of protection for sensitive information, such as private keys in crypto wallets.
The air gap principle involves physically separating a device or system from any network or internet connection to eliminate vulnerabilities. It ensures that there is no direct communication between the isolated system and online networks, thereby safeguarding against remote cyber threats.
Start securing your crypto journey today—visit Cypherock X1 to learn more.
Connect with us:
Twitter: @CypherockWallet
Telegram: Join the Community
